Introduction to CloudFront
Why is CloudFront important to developers?
What is CloudFront?
Amazon CloudFront is a fast content delivery network (CDN) service that securely delivers data, videos, applications, and APIs to customers globally with low latency, high transfer speeds, all within a developer-friendly environment
TL;DR:
- Full-site CDN
- Reverse proxy
- Globally distributed
- Cache
- Simple feature set
- Shared infrastructure
- “Serverless” (pay-per-request)
Reverse Proxy
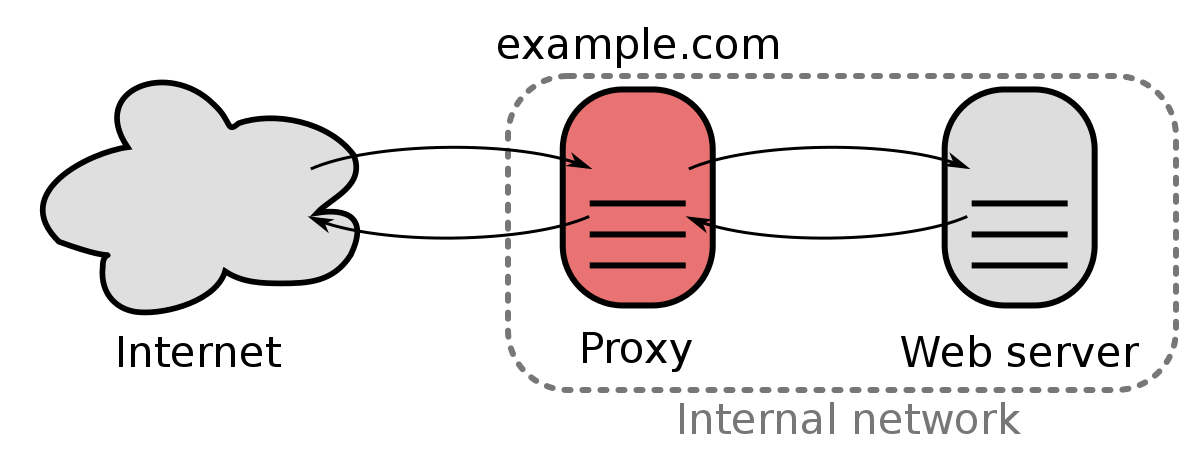
Globally Distributed
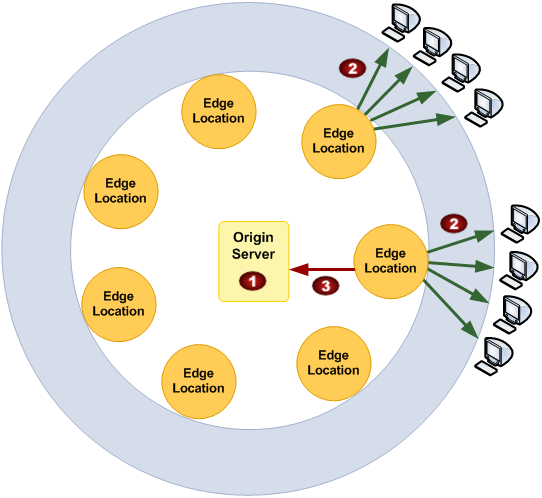
- Origin
- an endpoint that CloudFront forwards requests to, e.g. https://my-web-server.prod.example.com
Why use CloudFront?
- CloudFront offers a secure “front door” (DDOS protection, WAF attachment)
- Reverse proxy to route to disparate systems
- Cache is fast
Architecture for CloudFront
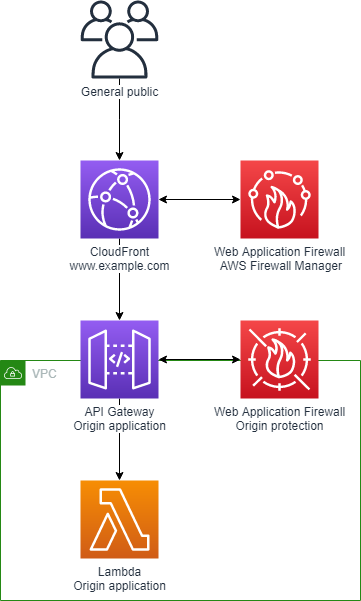
Configuring CloudFront
cloudfront.yml:
Resources:
CloudFrontDistribution:
Type: AWS::CloudFront::Distribution
Properties:
DistributionConfig:
CacheBehaviors:
- PathPattern: "/blog/*"
TargetOriginId: S3BucketOrigin
Compress: true
AllowedMethods:
- HEAD
- GET
ForwardedValues:
QueryString: false
Cookies:
Forward: false
Headers: []
MinTTL: 31557600
DefaultTTL: 31557600
MaxTTL: 31557600
ViewerProtocolPolicy: redirect-to-https
LambdaFunctionAssociations:
- EventType: origin-request
LambdaFunctionARN: !Ref TheOriginRequestLambdaFunctionVersionV2
- Cache behaviour
- a cache behaviour contains a path (e.g.
/blog/*), an origin (S3) and associated cache settings (headers, cookies, querystrings and TTLs)
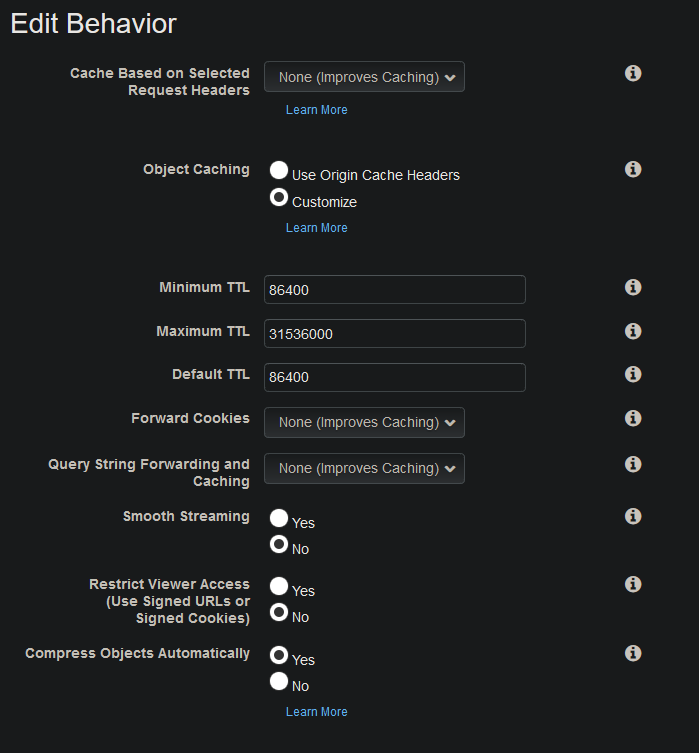
Whitelisting Headers

Cache Hash Configuration
URL + headers + cookies + querystring = cache hash key
For example:
/blog/my-first-post + {} + {} + []
- First request comes in, cache hash key is evaluated, no cache exists. Request is forwarded to origin.
- Response is received from origin, stored as response for cache hash key
- Second request comes in, cache hash key is evaluated.
- If it matches the first request; no request is made to the origin and the response is served from cache.
Path Patterns
- Exact or prefix match only
- Most specific match wins
TTLs
Two options:
- Set TTLs only in CloudFront
- Configure origin to return cache headers, also configure TTLs in CloudFront
you can configure your origin to add a Cache-Control max-age or Cache-Control s-maxage directive, or an Expires header field to the file
Invalidation
Testing
test_smoke_blog.py:
import os
import requests
cf_url = os.environ["CF_URL"]
def test_my_first_post_200():
r = requests.get(f"{cf_url}/blog/my-first-post")
assert "hello world" in r.text
assert r.status_code == 200
pytest test_smoke_blog.py:
[2020-08-17T01:58:59.408Z] ============================= test session starts ==============================
[2020-08-17T01:58:59.408Z] platform linux -- Python 3.7.8, pytest-5.4.3, py-1.8.1, pluggy-0.13.1 -- /home/ec2-user/.local/share/virtualenvs/test-AjaDab1m/bin/python
[2020-08-17T01:58:59.408Z] cachedir: .pytest_cache
[2020-08-17T01:58:59.408Z] collecting ... collected 1 items / 0 deselected / 1 selected
[2020-08-17T01:58:59.408Z]
[2020-08-17T01:58:59.788Z] test_smoke_blog.py::test_my_first_post_200 PASSED
[2020-08-17T01:58:59.788Z]
[2020-08-17T01:58:59.788Z] ======================= 6 passed, 3 deselected in 0.69s ========================